Introduction
There are a lot of risks implicated in the development of a new product. Developing an application or product is the essential measure for your company, as the whole business idea is set around it. Thus, companies take the MVP approach for releasing their business idea into the market.
There are four major approaches to developing an MVP, monolithic, service-oriented, microservices, and serverless architecture.
This blog will provide you with the correct insights into making the right choice for developing the product.
Monolithic Architecture
What is Monolithic Architecture?
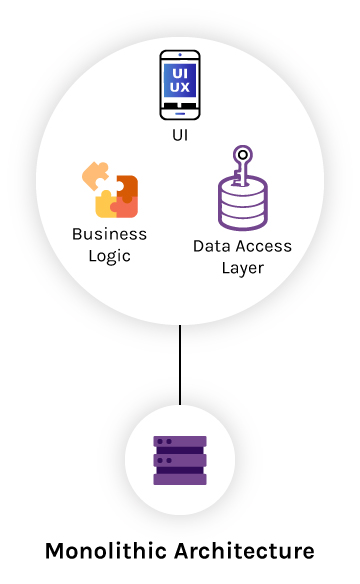
Monolithic architecture is a well-known structure for software applications. This traditional structure is a unified development model that refers to a single indivisible unit. Since all parts of the software are unified, the various components of the application and its services are combined and managed on a single platform.
Nowadays, Monolithic Architecture is rarely used because of its complex nature. But, if we just consider a minor example of an ecommerce SaaS application, which can contain a web server, a load balancer, a catalog service, an ordering system, a payment function etc, all coupled tightly together. They have huge code bases, and even a slight change in a single function can require compiling the testing of the entire platform. Initially Netflix, Uber, Airbnb, they all started with this architecture, but soon as they scaled, they switched to microservices.
Typically, a monolithic application comprises three components:
- Client-side user interface
- Server-side application
- Data interface
Pros of Monolithic Architecture
- Suitable for SMBs
If you don’t want to spend a big budget on your business idea or you require a simple approach for your MVP, then monolithic architecture is your best choice.
- Easy development
In Monolithic Architecture, all development steps take place in a single directory. Since developers can deploy changes or updates independently, it gives them the option of easy deployment, which saves them a lot of time. It also allows the integration of several tools supporting MVP development services.
- Simple Framework
This infrastructure enables easy monitoring by maintaining the front-end, back-end and database simultaneously for multiple processes.
- Improved Performance
An adequately adopted monolithic architecture approach works relatively faster than microservice-based applications. It enables faster communication between software components thanks to shared code and memory.
- Data Integrity
Monolithic architectures benefit from the various data integrity mechanisms and direct transaction controls managed by RDBMSs, as they typically use a single database for storage.
Cons of a Monolithic Architect
- Not Suitable for Complex Software
Software is constantly growing as technology changes. A monolithic, traditional approach is more difficult for developers to maintain.
- Poor Modular Structure
Any changes in the logic of one module lead to changes in the codes of other modules, making the whole monolithic approach to be rebuilt for deployment. Failure at a single point can also bring down the entire system.
- Agility Issues
In a monolithic architecture, a slight change request leads to a complete relocation to an agile work environment. Because the team is structured for development, the task is shared between them, and when an update request comes, it affects the work of the entire team and significantly reduces agility.
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA)
What is Service-Oriented Architecture?
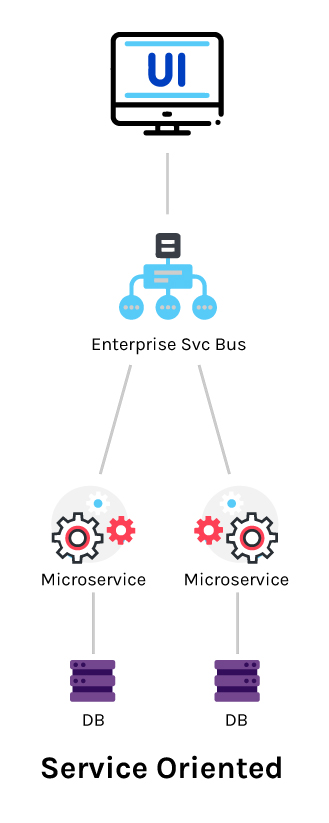
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) is a software architecture type that is composed of discrete and loosely coupled software agents employed to perform its function.
SOA has two principal functions that can be played by a software agent:
- Service Provider: It is a software body that executes a service request.
- Service Consumer: It can be another service or an end-user application that calls a service provider.
An SOA concept does not have limitations in the programming language or platform. This design pattern builds distributed systems that follow the protocol to deliver services to other applications.
This model uses a message-based communication model to communicate with applications and other services, and its modules are seamlessly integrated and can be easily reused.
SOA is a modular way of breaking up monolithic applications into smaller components. They are frequently used for enterprise level services because of their modular nature. Some of the most common examples would be healthcare services, Situational Awareness Systems (SAS) used by militaries and air forces, GPS service in mobiles, etc.
Pros of SOA
SOA has the following advantages:
Easy to Maintain
As the software services are platform-independent in SOA, it is easy to update and manage them without affecting other services.
Reliability
Services are small compared to the vast code fragments like in the monolithic approach, making the debugging process easy and SOA-based products more reliable.
Manage Complexity
The implementation is transparent in SOA due to service specification integration, isolating the complexities and making the process more manageable.
Reusability
It enables service implementation without influencing other applications or services because of its self-contained and loosely coupled nature of functional components. Thus, it facilitates the advantage of the reusability of services without affecting other services.
Parallel Development
Service-oriented architecture follows layer-based and loosely coupled architecture, due to which it supports parallel development. This enables all the independent services to be developed and completed at the same time.
Cons of SOA
Greater Load
In a service-oriented architecture, services require full validation of all input parameters during each interaction among them. Therefore, it increases the load when using multiple services, decreasing overall performance and prolonging the response time.
Complex Service Management
While executing a task in SOA, services have to exchange messages constantly. And, when the number of those messages gets overwhelming, it becomes challenging to manage those services simultaneously.
SOA increases the flexibility for building and deploying applications for complex enterprise systems. Microservices offer a more fine-grained approach to accomplishing the same aim, and breaking monolithic applications into smaller components is impossible. Hence, SOA is the best approach to develop complex projects, having unique needs and use cases, into isolated independent services.
SOA can be a quantifiable choice for developing an MVP. You can read our Minimum Viable Product (MVP) Development Guide for a better understanding of the process.
Microservices Architecture
What is Microservices Architecture?
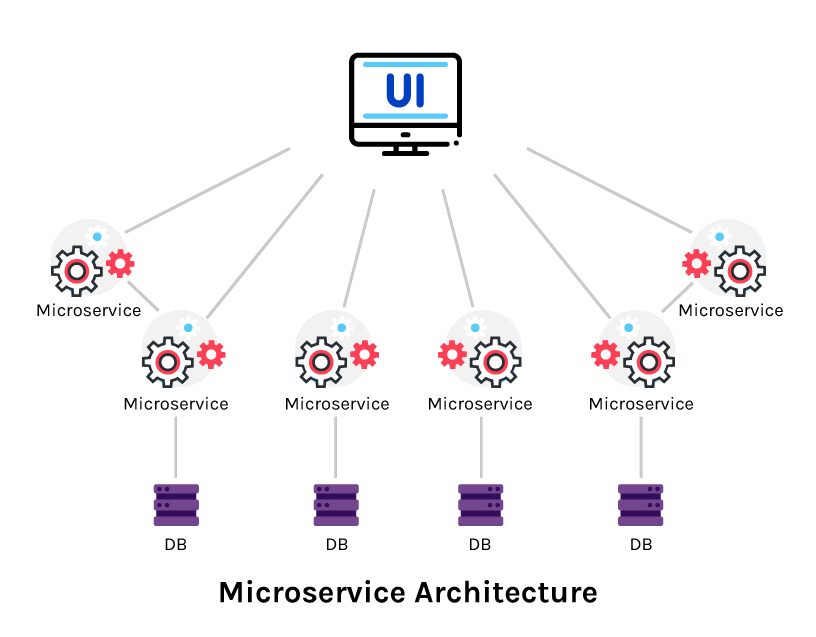
It is a type of Service-Oriented Architecture. A suite of small services combines to construct a complete service in the microservices’ architecture. It incorporates many microservices that communicate with each other. The microservice architecture comprises multiple independent services created around business capabilities that are combined through APIs.
While the microservices architecture is composed of many loosely coupled and independently deployable minor services, it does not reduce the complexity of a system. Instead, it enables the system complexity to be more visible and manageable.
Microservices are like an enhanced or strengthened way of SOAs, because while SOA breaks down the application on a modular level, microservices break it down at a fine-grained level. One of the best examples would be NETFLIX. In 2008, they experienced a major database corruption, which made them realize they need to move from their monolithic architecture towards a more scalable approach. In 2009, they began to refactor their monolithic architecture, service by service, into microservices. They spent the next 2-3 years migrating their entire services and completed it in 2012.
Pros of Microservices Architecture
Ease of development
One of the significant advantages of microservices is that it comprises small services that are independent of each other, loosely coupled; thus, they can be developed and deployed independently.
Rectify Agility Issues
Since the architecture is divided into small units, you don’t have to work on the whole app at once and hire several teams to work on different services independently. It speeds up the development process and product release.
Scalability
You can use multiple languages, frameworks, and technologies to develop the microservices architecture. Also, this architecture supports horizontal scaling, which allows developers to scale the different parts of the services dynamically. Therefore, you will launch and develop the app promptly.
Cons of Microservices Architecture
Development Cost
Since microservices have a higher load of services, deployment, and monitoring, this results in higher operational overhead, resources, and remote calls, which can lead to increased development costs.
Complexity Issues
Complexity is one of the significant issues with Microservices Architecture. Since it split the product into independent microservices, it became difficult to manage. From design to technical development and implementation, it requires enormous efforts, such as team resources, skills, and planning.
Also, using multiple programming languages for different operations within the development process becomes harder to switch.
Security Issues
Another issue in Microservices Architecture is not implementing proper security measures. All the services communicating via APIs externally make the product vulnerable to a potential attack.
Microservices’ architecture is excellent for large-scale products and complex systems, with the potential to scale. If you have a high budget set up to spend on MVP development costs and a large development team, you can choose this architecture that will break your complex app into small services.
Serverless Architecture
What is Serverless Architecture?
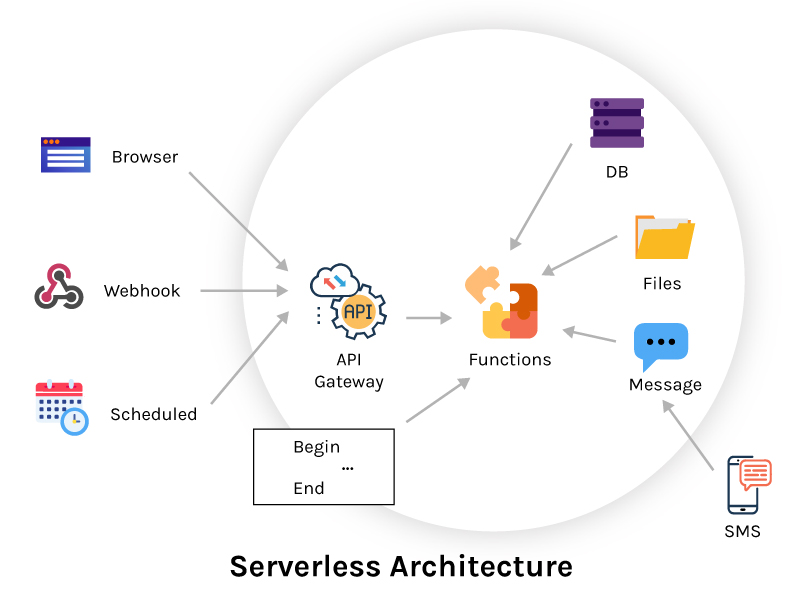
A Serverless architecture approach harnesses cloud computing technology to develop and run applications and services. This type of architecture goes beyond Microservices and manages the code execution and deployment without bothering server conditions and infrastructure management.
A third-party cloud service like AWS manages the server maintenance and provision process. The application running on servers eradicates the requirement for additional resources and databases.
Serverless Architecture allows applications to be hostless, stateless, easy to scale, and event-driven. The Cloud Providers, like Amazon, allow you to run your application defining no infrastructure. There are many Cloud Providers that give you this feature, like Lambda by AWS, Google Cloud Functions, IBM’s OpenWhisk, etc. Some of the famous organizations that follow serverless architecture are Slack(Marbot), Coca-Cola, which now uses AWS Lambda for transaction related services in their Vending Machines.
Pros of Serverless Architecture
Easy Development and Deployment
Since the developers do not have to worry about the infrastructure, database, and resource management, developers can focus on code execution and speed up the deployment process.
Cost-Reduction
You can reduce the development cost in serverless applications as you don’t need to handle databases, extra resources, and manage servers. The only things that cost some charges are the used CPU cycles and memory. Thus, you can develop quality code at minimum expense.
Scalability
A business that requires an approach where they can scale their product further; serverless is a suitable architecture for them. It allows automatic and seamless scaling through Serverless computing. As the increment of your load, resource request, or user base does not affect your development process; it enables the automatic scale of your application.
Cons of Serverless Architecture
Tight-Coupling
We cannot build substantial chains of functions as it can complicate the architecture and infrastructure. Also, it makes it difficult to establish the interaction of separate modules, resulting in the same issue as monolithic architecture.
Migration challenges
As you provide complete control of your operations to a vendor, it becomes challenging to migrate from one vendor to another and limit the business logic changes.
Not suitable for long-term tasks
A serverless app will need extra FaaS functionality if a task takes more time to process. Thus, it is not suitable for long-term functions.
Serverless software architecture can be suitable for fast-growing applications and requires rapid change with additional resource support. These days, we can observe many modern applications benefit from the serverless approach for the products that need limitless scaling and are client-heavy apps.
If you are planning to hire an MVP development company, you can consult their software specialists to follow the best development architecture for your project.
How Can CodeStore Technologies Help You?
At CodeStore Technologies, we offer dedicated MVP development services, in which we implement various models of minimum viable products. We select suitable MVP development models and fabricate the complete digital product as per the budget and requirement of the clients.
We establish communication between the services of your MVP and enable load balancing, scaling up and downing of services.
We provide innovative MVP development solutions suitable for your business’s size and product ideas. CodeStore is a leading mobile and web app development company in India, Canada, and the USA. We are a leading mobile and web app development focusing specially on providing the most effective digital transformation services.
With the help of our well-versed and skilled team of developers, we have delivered several projects in many industries.
Get in touch with us and share your queries with us at: sales@codestoresolutions.com or you can call us at:- +91 8069195500 | +1 (302) 520-2820

