table of content
Legal Issues to consider while developing a Mobile App
 Mobile App development is gradually becoming one of the most significant for generating revenues for small and start-up tech companies. But despite this rising popularity in app usage and development, developing a mobile application is difficult. There are several key legal considerations of structuring the thing before developing an everlasting and successful product.
Mobile App development is gradually becoming one of the most significant for generating revenues for small and start-up tech companies. But despite this rising popularity in app usage and development, developing a mobile application is difficult. There are several key legal considerations of structuring the thing before developing an everlasting and successful product. To protect their rights and reduce the risks of liability from violating others’ rights, companies should consider and address legal issues from the beginning and throughout the mobile app development.
We, the Codestore team, have created a general list of some of the general legal considerations relevant to developing a mobile app.
So, what makes an app legal?
Non-Disclosure Agreement
A non-Disclosure Agreement is a contractual document under which the parties legally pledge to keep certain information confidential. NDAs can be Unilateral, Bilateral, or Multilateral.>
An NDA agreement for app development has no guarantee that it has ensured the business idea, but it will significantly help in taking legal action against anyone who violates the terms of it.
That being the case, signing a non-disclosure agreement for software development is a way to protect the idea or the fact of utilizing outsourcing as a total.
Intellectual Property Rights
The intellectual property related to a mobile app can include source codes, components, and contents such as graphics, texts, audio, videos, and other types of information. While developing and distributing a mobile app, a company must address both protecting its IP rights and minimizing its risk of violating the IP rights.
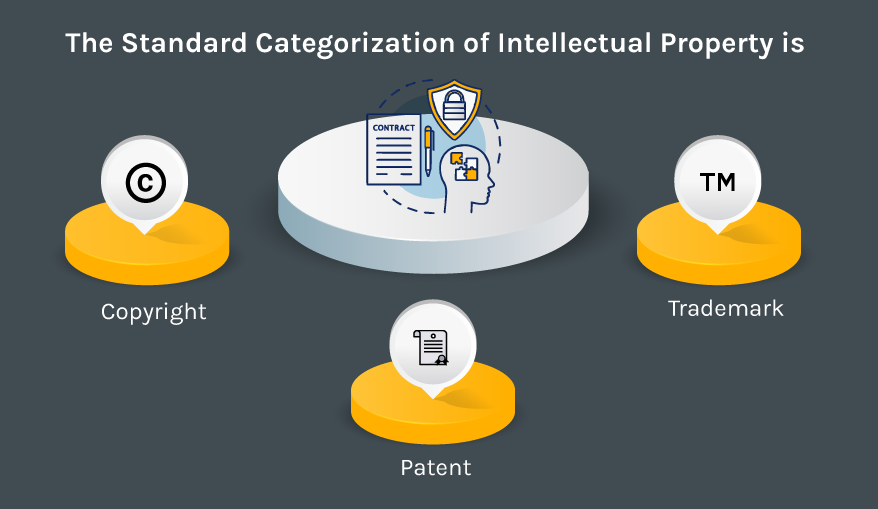
The standard categorization of intellectual property is copyright, patent, and trademark.
Copyright
It secures the original work against illegitimate copying or reproduction. This security usually includes source code, exclusive images, graphical user interface elements, artwork, and contents written.
Patent
A patent is not a usual practice among app developers, partially due to patent rights requiring long application processes that could take years and are too costly. A mobile app may have a patentable unit to it for certain processes or methods integrated with the app.
Trademark
Trademarks are source identifiers for particular products or services such as the app’s name, logo, and slogan. It is standard practice that most development companies register at least their name of the app as a trademark.
Jurisdiction
Before marketing and distributing an app abroad, a person must ensure that a future product complies with local laws. The cross-border nature of the Internet may cause copyright/trademark issues in other countries. Above all, it originally might not be so in the home country.>
Also, they must know any data and consumer protection laws that countries apart from their home countries might have. If a company is planning to set a product in motion in a foreign land, it must hire a lawyer to understand the essence of other countries’ legal policies.
Privacy Policies and Data Security
Privacy Policies are necessary legal considerations in mobile app development. With collecting users’ data, the responsibility is to include a privacy policy, be transparent with users about what data you may access and why it’s needed. The company must assure people they protect users’ personal information and keep it secure.
Data Collected by a mobile app is far more precise for target advertising as compared to website data. Thus collection, storage, and protection of data is a sensitive area and needs to be addressed with caution. From a pure data protection point of view, an app is subject to identical guidelines as websites and other online businesses. App developers must ask themselves whether their app collects data such as the name, contact details, location, unique I.D., or other information on the users.
Term of Use
Terms of Use is a legal agreement that the app developers are entering with every user of the app. It tells about what the app is, how the user must use it, what are the improper or unlawful use of the app, and the outcome of improper use. For this reason, prior user acceptance is essential. A term of use agreement is crucial because it limits the possibility of legal and ethical issues for mobile apps if a user misuses the product.
End-User License Agreement (EULA)
As with privacy policies, the app stores require apps on their platform to have an end-user license agreement or EULA. This is a contract between the owner of the app and the users of the app. We sometimes refer to these EULAs as shrinkwrap or click-through agreements.
Implementing a EULA will protect the IP and investments because it acts as both a copyright license and a contract. This creates the backbone of every form of software usage at the end level.>
The goal with a EULA is to ensure the user is not misusing the app, to jeopardize the company’s ownership of the IP embedded in or otherwise connected to the app.
A EULA appears before the user installs software. To complete the installation, a window pops up with multiple screens of texts. The user scrolls to the bottom of each page and clicks the “I Agree” button.>
App Stores Agreements
The last and most important item in the App development process is the App’s legality. Delivery of mobile apps to end-users usually happens through app stores. Agreements highlight the security of personal data, such as health information and information collected from minors. Moreover, these are intellectual property issues relating to mobile products.
The mobile app must meet all the criteria for app publishing outlined in Google’s guidelines and Apple’s guidelines. These platforms also secure the right to alter the app’s legal terms or add additional clauses when necessary.
What does CodeStore follow legal requirements while developing a mobile application?
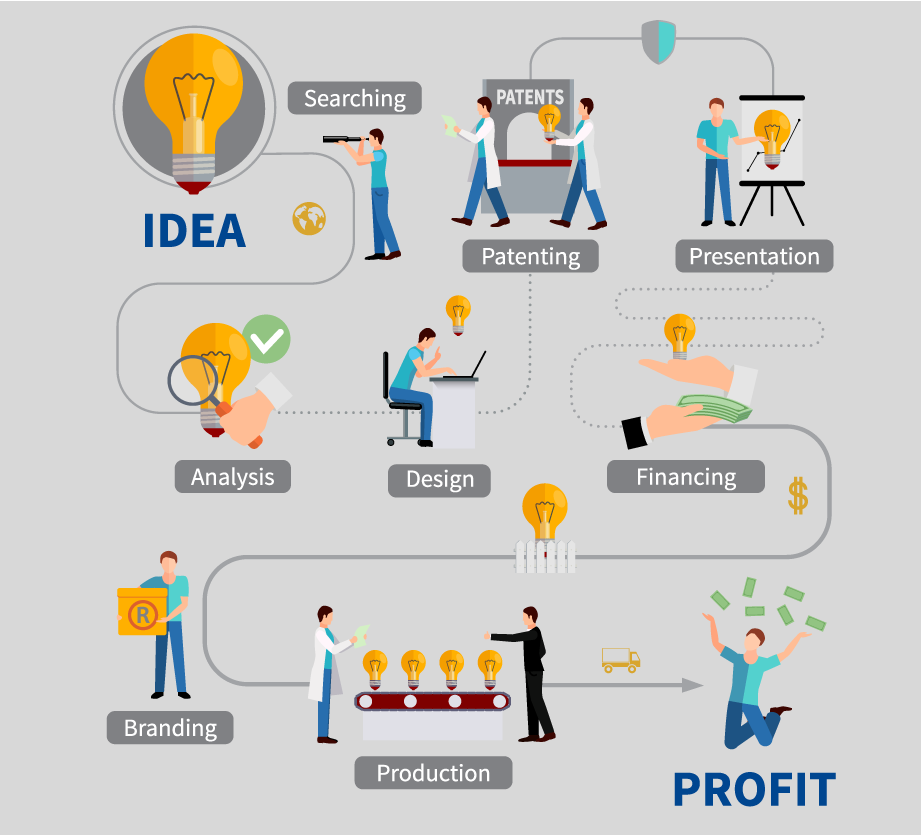
Here are a few steps we consider following during the scope of work in the application development:
- Codestore comfortably up-lifts our clients to sign a non-Disclosure Agreement before discussing the idea of the application.
- We unveil every practice regarding collecting, using, and protecting personal information in our Privacy Policy
- We sign the Master Service Agreement (or MSA) with the client that establishes what terms and conditions will govern all current and future activities and responsibilities between the two parties.
- Our main motto is to maximize outcomes on investments and leave our clients satisfied and coming back for more.
Bottom Line!
Mobile app development is an overcomplicated and multi-branched process. A wise legal strategy is a go-along strategy in the app development process. This will help to minimize the legal risk and protect your intellectual property rights.>
App development is a fun, fast-paced, and exciting business. But just like other businesses, it comes with serious legal issues that you must know and deal with properly to minimize your liability and achieve success. Development companies must protect their rights, clients’ interests, and investments by efficiently and thoroughly addressing legal matters. Establishing adequate legal and compliant strategies is paramount to minimize liability risks inherent from violating others’ IP rights, app store agreements, and territorial laws. This directly leads to increased responsibility of the developers to be not only diligent while debugging and coding, but also the legal side of their development, simply because of their popularity.
At Codestore, we are always aware of legal matters concerning your apps and are always at the forefront of the latest requirements and laws to improve our products and durability. We provide enterprise-grade software solutions for small, medium, and large-scale enterprises to understand legal issues related to their app.
[number]




