table of content
- Introduction
- What is Blockchain?
- The Evolution of Blockchain Technology
- Features of Blockchain
- Types of Blockchain
- Public Blockchain
- Private Blockchain
- Consortium Blockchain
- Hybrid Blockchain
- Use Cases of Blockchain
- Supply Chain Management
- Healthcare Records
- Decentralized Identity Verification
- Smart Contracts and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- Digital Voting and Governance
- Intellectual Property and Royalties Management
- Real Estate Transactions
- Energy Trading and Grid Management
- Charity and Nonprofit Transparency
- Educational Credential Verification
- Challenges and Considerations
- Future of Blockchain
- Final Thoughts
- FAQs
How Can Businesses Leverage Blockchain Beyond Bitcoin?

Introduction
Most people automatically think about Bitcoin whenever they hear the term “blockchain”. The forefront popularity of Bitcoin exposed blockchain technology, while other diverse applications of blockchain technology demonstrate its extensive potential. The abilities of blockchain extend past cryptocurrency storage to bring operational transformation into numerous market sectors. Blockchain can transform current thinking about data storage and trust relationships by achieving new operational standards.
This blog will provide you with an extensive knowledge of blockchain technology by discussing its definition, types, challenges, and blockchain technology use cases.
What is Blockchain?
The fundamental operational principle of blockchain functions as a distributed ledger technology (DLT), that executes transactions across multiple computer systems in a tamper-proof fashion and provides complete operational transparency. The decentralized structure which ensures no point of failure exists makes blockchain technology both resilient and trustworthy. A chain block holds three components: the transaction data and timestamp alongside a cryptographic verification that binds it to the preceding block to keep data pure.
The Evolution of Blockchain Technology
Since its origins with Bitcoin in 2008 blockchain technology has grown at a quick pace. The Bitcoin network began with cryptocurrency security but has now expanded to serve many broader applications throughout the technology world. Ethereum’s 2015 launch demonstrated smart contracts which activated decentralized applications (Dapps) to modify various sectors particularly financial institutions and supply chain businesses.
Enterprise blockchain solutions emerged during this period when Hyperledger and Corda provided business-oriented permissioned blockchains for organizations working toward privacy along with better scalability options. Ethereum fixed its scalability limitations through Proof-of-Stake (PoS) integration and Layer 2 technology enabled the Lightning Network development. The evolution of blockchain technology enables multipurpose usage across social impact fields with sustainability and decentralized finance and addresses global issues.
Through reduced transaction costs and amplified supply chain transparency while offering decentralized governance blockchain technologies transform business operations and revolutionize how we handle data. Although scalability issues along with energy use and regulatory obstacles remain current challenges blockchain maintains a promising future. Modern applications built on improved interoperability will leverage blockchain technology to transform financial systems and healthcare platforms and every aspect of human interaction as we know it.
Features of Blockchain
- Decentralized: Blockchain operates without a centralized control structure since data exists over a network of connected computers. Every computer in a distributed network maintains the full version of blockchain data.
- Immutable: New data submitted to the blockchain becomes immutable because modification or alteration of existing data remains impossible. The system guarantees both high reliability and security through its design.
- Transparent: Blockchain allows anyone to view the data and transaction history. While changes can be seen and verified, they cannot be altered.
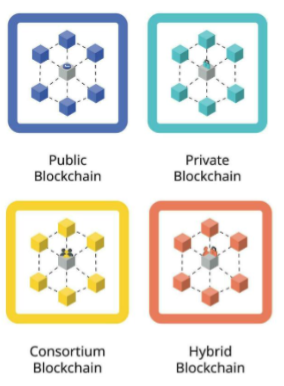
Types of Blockchain
Public Blockchain
Public blockchains are open and decentralized. Anyone with an internet connection can access it. They ensure trust, security, and privacy, but they process slowly and consume a lot of energy. They increase decentralization and accessibility but lack central authority, which makes it difficult to execute and follow regulations.
Example: Bitcoin, Ethereum.
Private Blockchain
Private blockchains are closed networks that only authorized individuals can access. They are perfect for businesses because they provide scalability, improved privacy, and faster transactions. They are more centralized but sometimes raise queries regarding trust and security. A small number of nodes can make them vulnerable to manipulation or system failure.
Example: Hyperledger, Corda.
Consortium Blockchain
Consortium blockchains are maintained by multiple alliances, which improves speed, security, and flexibility while maintaining partial decentralization. They enhance cooperation, but they slow down decision-making because they demand everyone’s consent. Their highly regulated structure ensures privacy, but if governance is not properly guaranteed, it could create risks to transparency.
Example: Energy Web Foundation.
Hybrid Blockchain
Hybrid blockchains mix public and private elements to balance accessibility and security. They are flexible, cost-effective, and highly secure, but it can be difficult to maintain efficiency and credibility. While they provide restricted data access, their closed ecosystems may limit opportunities for wider collaboration and present transparency issues.
Example: IBM Food Trust.
Use Cases of Blockchain
Supply Chain Management
Using Blockchain provides supply chains with the ability to track products while maintaining visible records that cannot be altered. Leveraging blockchain technology provides businesses with real-time tracking capabilities that support product authenticity tracking and inspire compliance adherence in operations like food safety and pharmaceuticals and luxury goods.
Healthcare Records
A blockchain system creates a secure storage solution for medical records which permits authorized healthcare providers to access the latest patient information. A blockchain system enables safe medical data storage and sharing which results in better patient care while decreasing medical errors and enhanced communication across health facilities.
Decentralized Identity Verification
Blockchain technology enables persons to regulate their digital identity data. People can carry out minimum data exchanges with outside parties when proving legal age status while protecting both their privacy and minimizing identity theft risks.
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Vehicle Polaris combines infrastructure with law to form self-implementing agreements that execute terms automatically when designated rules become active. The underlying structure of DeFi applications functions through blockchain technology which allows users to transact P2P without dependence on conventional financial entities.
Digital Voting and Governance
Through blockchain technology organizations can build a secure system for online voting which offers transparent verification. If votes are immutable and easily verifiable blockchain enhances faith in election results and helps organizations and local governments lower the administrative effort of running elections.
Intellectual Property and Royalties Management
Artists and writers together with creators can register their intellectual property on blockchain systems to both demonstrate ownership and optimize royalty distribution procedures. A blockchain registration system enables creators to demonstrate ownership and prevents piracy along with fulfilling fair revenue sharing for artists.
Real Estate Transactions
Blockchain technology optimizes real estate transactions including purchases, sales, and leases by providing a single verified information source. The use of blockchain establishes a validated central registry of property records which leads to reduced incidents of deception and faster sales with decreased costs because intermediary intermediaries are eliminated.
Energy Trading and Grid Management
Through blockchain technology peer-to-peer energy trading markets enable the transparent monitoring of renewable energy production and distribution among network participants. Solar panel owners would directly market their excess electricity through a tamper-resistant automated marketplace to their neighbors.
Charity and Nonprofit Transparency
The implementation of blockchain increases charitable organization transparency since it displays precise usage details regarding donor money distribution and expenditure. Transparency through blockchain creates environments of trust which promotes a greater number of donations.
Educational Credential Verification
Blockchain technology offers universities and training institutions an opportunity to distribute diplomas along with certifications and transcripts to students. Employers benefit from simple credential verification through blockchain certification while certification records remain permanently protected from the risk of modification loss.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its immense potential, blockchain faces several hurdles:
- Scalability: Current blockchain networks struggle with handling high transaction volumes.
- Energy Consumption: Proof-of-Work (PoW) blockchains demand significant amounts of energy for their operation.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Existing regulations for blockchain application control remain uncertain across all nations as governments continue their search for solutions.
- Integration: Technological implementation of blockchain within existing corporate infrastructures requires both time allocation and organizational funding.
Future of Blockchain
The future of blockchain is bright, how can I say that?
Today’s cryptocurrency systems run through multiple applications of blockchain technology. Bitcoin stands among the most widely used cryptocurrency systems available today. Everyone understands bitcoin so its introduction can be bypassed. Additional industries need to leverage blockchain technology as their core capability.
The Finance and banking sector will experience significant transformation through Blockchain technology because it delivers an incredibly reliable system for managing financial transaction data. The quick transaction speed of Blockchain delivers secure financial operations which gives positive indications for future banking applications.
Blockchain technology can help to reduce fraud to a higher extent and enhance privacy. The identity of transaction participants is replaced with an alias. Blockchain technology has a bright future in the healthcare sector as well. It can store the patients’ records securely without compromising the privacy of patients.
Final Thoughts
Bitcoin functions as one implementation of the many applications of blockchain technology, not a whole. This adaptable technological framework shows the capability to reshape various sectors and create universal enhancements across worldwide populations. In our data-oriented age blockchain functions as an essential innovation that provides trusted transparency for critical matters. Our exploration of blockchain possibilities reveals endless opportunities for the future.
CodeStore can help you unlock the possibilities of blockchain! We create scalable, safe, and customized blockchain solutions for your business. Boost efficiency, trust, and transparency. Visit us at https://codestoresolutions.com/ right now to transform your business!
FAQ
What is blockchain technology, and how does it work?
Blockchain is an encrypted digital record that safely logs transactions across several nodes without the need for intermediates. It prevents tampering and ensures the security and authenticity of data.
What are the key advantages of blockchain beyond cryptocurrency?
Blockchain makes business operations accessible, secure, and efficient. Industries are revolutionized by it because it makes smart contracts, decentralization, and fraud protection possible.
What are the different types of blockchain networks?
The many types of blockchain networks: public, private, consortium, and hybrid. Each has its own pros and cons and offers various levels of security and decentralization.
How does blockchain enhance security in business operations?
Blockchain uses consistency, decentralization, and cryptographic encryption to provide security. It is perfect for financial services, contracts, and sensitive data since transactions are inaccessible, minimizing fraud, illegal access, and data breaches.
How can blockchain improve supply chain management?
Blockchain provides real-time tracking, minimizes fraud, and boost transparency. It guarantees accurate and unchangeable records of product movement, which lowers inefficiencies and boosts trust among all.
How does blockchain improve identity management?
Blockchain lowers the risk of identity theft by enabling safe, autonomous digital identities. Users have control over their data to simplify authentication for banking, healthcare, and other services.
Can blockchain improve healthcare data management?
Yes, blockchain guarantees safe, unchangeable patient records that preserve privacy while enabling authorized access. It improves data integrity in research and healthcare systems, decreases medical errors, and increases interoperability.
What are the challenges businesses face when implementing blockchain?
High implementation costs, scaling problems, unclear regulations, energy consumption, and interaction with current systems are some of the challenges. Businesses must analyze compliance and profitability before implementing blockchain technologies.
What is the cost of implementing blockchain in business operations?
The type of network, level of development complexity, and safety concerns all affect how much it costs to implement blockchain. Simpler ones begin at $10,000 to $50,000 and more complicated ones can cost anywhere from $50,000 to millions.
How can businesses get started with blockchain development?
Businesses should establish their use cases, select the appropriate blockchain type, collaborate with competent engineers, and ensure regulatory compliance.